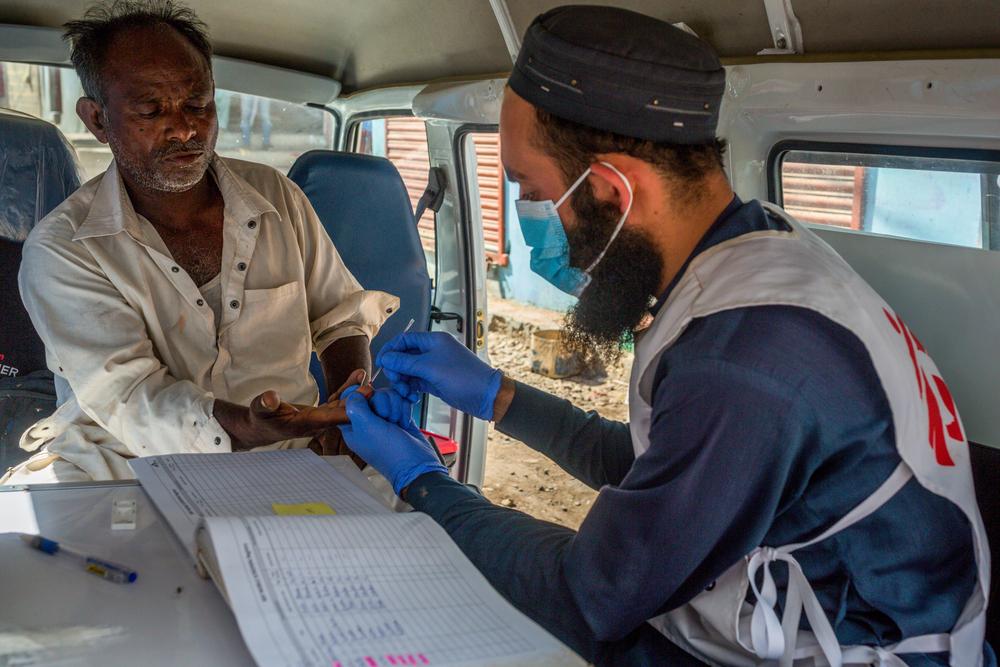
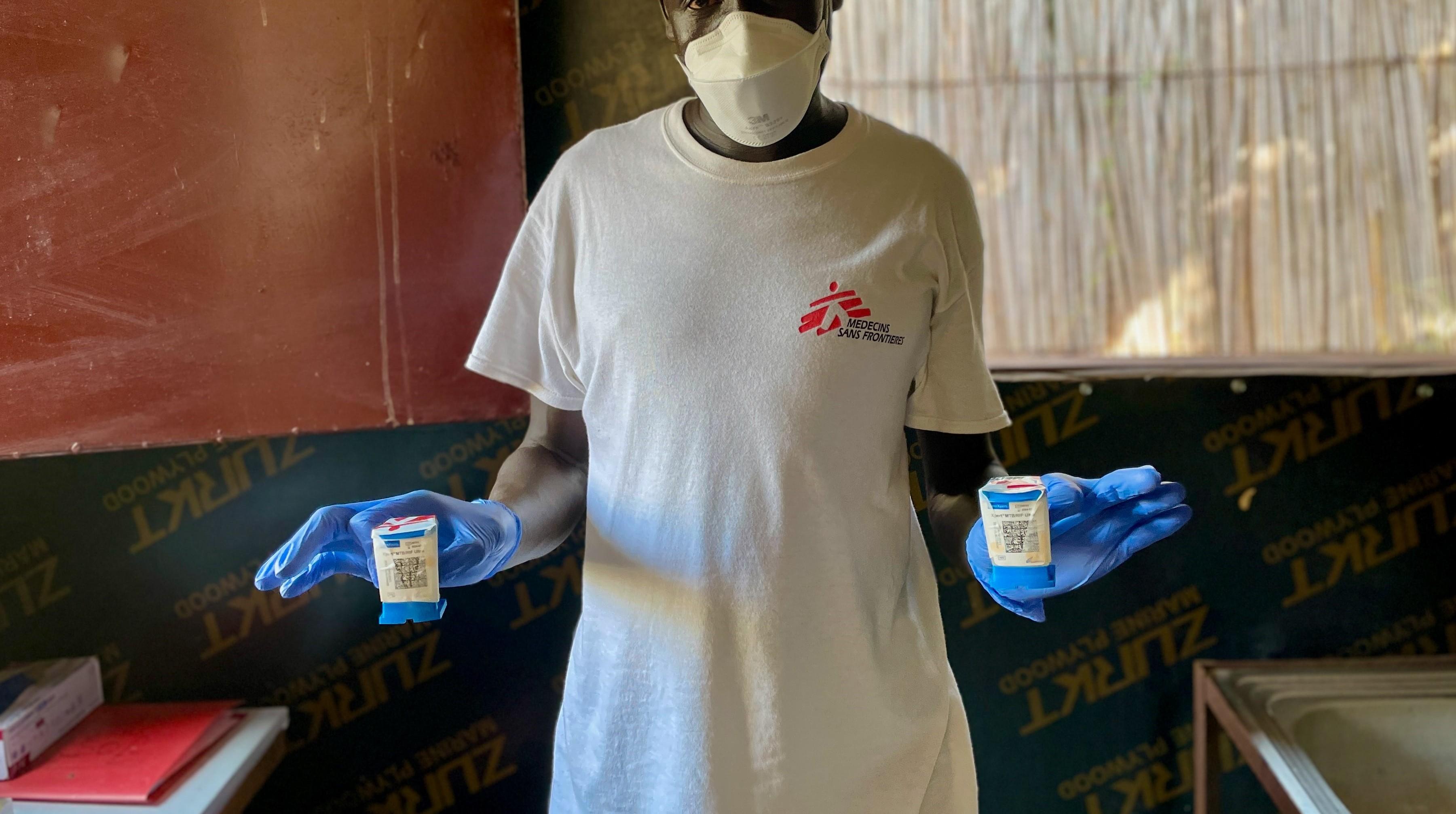
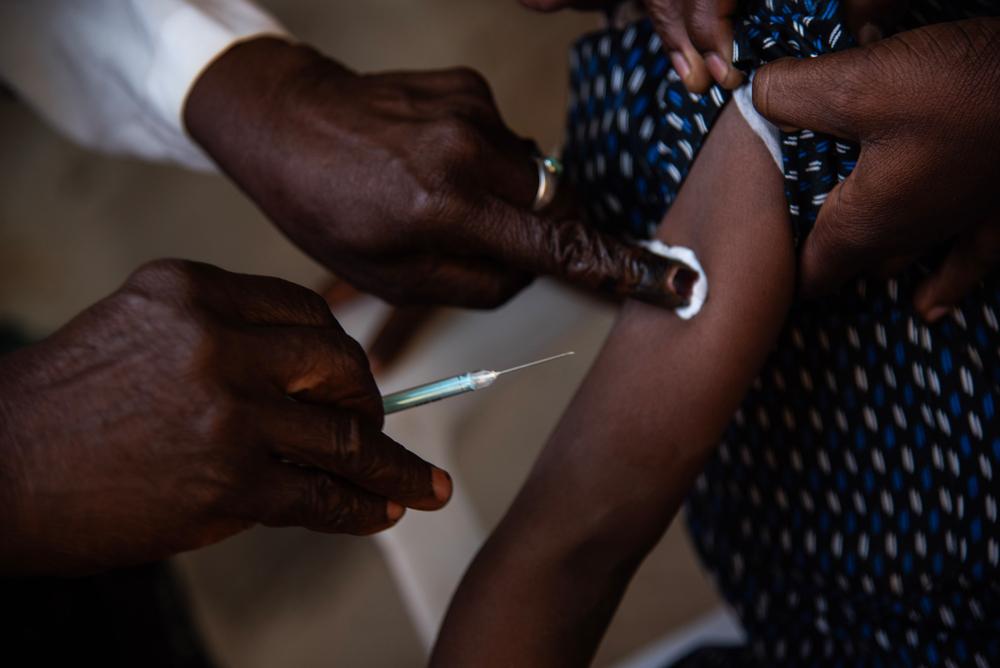
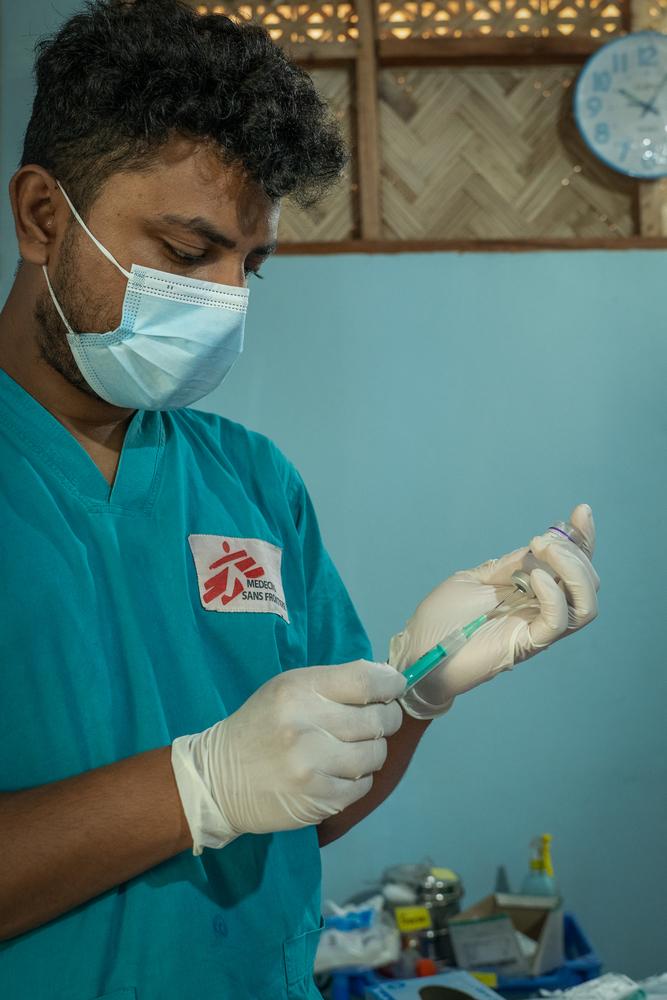
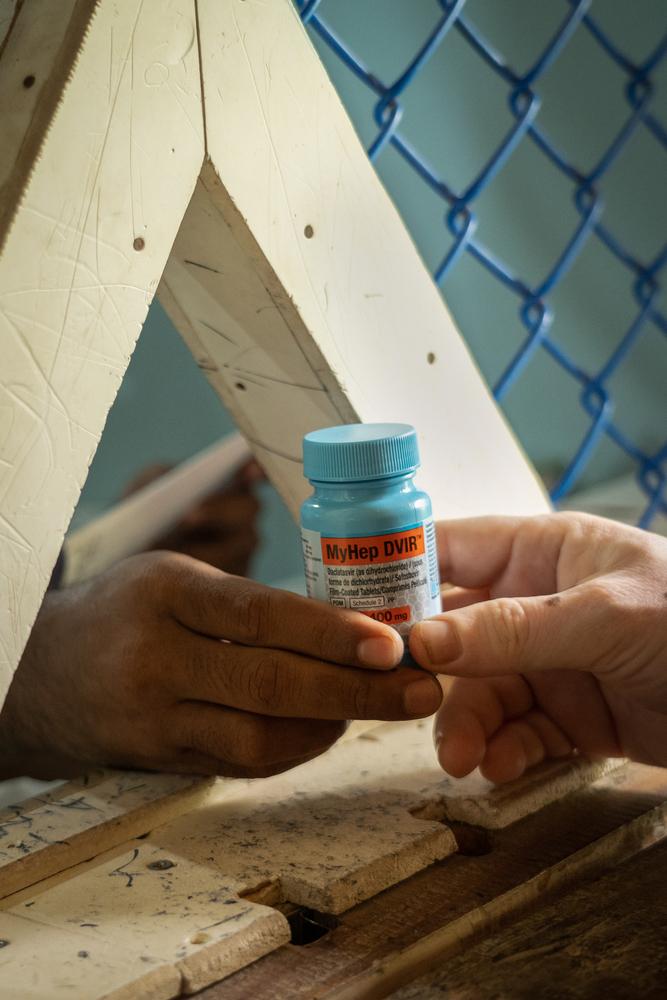
Viral Hepatitis has become a public health challenge of global proportions.
Hepatitis infection is an inflammation of the liver that is caused by a variety of infectious viruses and noninfectious agents leading to a range of health problems, some of which can be fatal. There are five main strains of the hepatitis virus, referred to as types A, B, C, D and E. While they all cause liver disease, they differ in important ways including modes of transmission, severity of the illness, geographical distribution and prevention methods. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), in particular, types B and C lead to chronic disease in hundreds of millions of people, especially in Africa, and together are the most common cause of liver cirrhosis, liver cancer and viral hepatitis-related deaths. An estimated 354 million people worldwide live with hepatitis B or C, and for most, testing and treatment remain beyond reach. Doctors Without Borders (MSF) strives to provide access to these measures across the world.